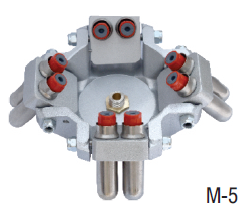
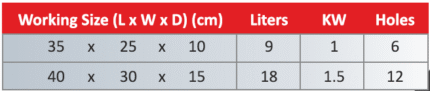
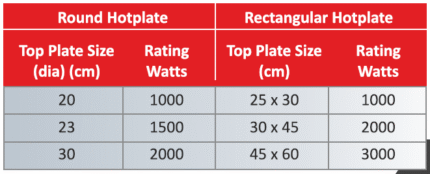
A Cube Mould 150x150x150 (Non-ISI) is a specialized tool used in the construction and civil engineering industries for preparing concrete test specimens. These specimens are typically tested for compressive strength, which is a crucial parameter in assessing the quality and durability of concrete. Here’s a detailed description of its features and typical uses:
Key Features:
1. Material :
– Cast Iron or Mild Steel : Typically made from high-grade cast iron or mild steel, which provides the necessary strength and durability to withstand the pressures exerted during the compaction and curing of concrete.
– Non-ISI : Indicates that the mould does not conform to the standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (ISI). It might be used in non-critical applications or where adherence to ISI standards is not mandatory.
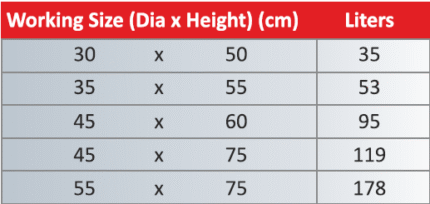
2. Dimensions :
– Internal Size : 150 mm x 150 mm x 150 mm (6 inches x 6 inches x 6 inches).
– External Size : Slightly larger due to the thickness of the walls.
3. Design :
– Split Design : Often designed in two halves (split mould) to facilitate easy removal of the cured concrete cube without causing damage.
– Base Plate : Includes a detachable base plate on which the mould is assembled. The base plate provides a level surface for casting and compacting the concrete.
– Bolts and Wing Nuts : Equipped with bolts and wing nuts or screws to secure the two halves of the mould together during the casting process.
4. Usage :
– Concrete Specimen Preparation : Used for casting concrete cubes to test the compressive strength of the concrete mix.
– Compaction : Concrete is poured into the mould in layers, and each layer is compacted either manually with a tamping rod or using a vibrating table to ensure there are no voids.
– Curing : After compaction, the concrete is allowed to set and cure, usually for 24 hours, before the cube is demoulded and further cured in water for a specified period (usually 7, 14, or 28 days) before testing.
5. Applications :
– Quality Control : Used in construction sites and laboratories to ensure that the concrete mix meets the required strength specifications.
– Research and Development : Employed in R&D to study the properties of different concrete mixes and additives.
– Education and Training : Utilized in educational institutions for teaching concrete testing methods and techniques.
6. Maintenance :
– Cleaning : Requires thorough cleaning after each use to remove any concrete residue and prevent rusting.
– Inspection : Regular inspection for any wear or damage to ensure the mould maintains its shape and integrity.
Advantages:
– Durability : Made from robust materials to withstand repeated use and the stresses of concrete compaction.
– Ease of Use : Split design with bolts or wing nuts facilitates easy assembly, disassembly, and removal of the cured concrete cube.
– Accuracy : Provides precise dimensions for preparing standard-sized concrete test specimens.
Limitations:
– Non-ISI : Being non-ISI, it may not meet specific regulatory or quality standards required for certain critical applications.
– Weight : Can be heavy and cumbersome to handle, especially in field conditions.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.